
Research in Photovoltaic & Solar Energy Materials
Several concurrent research projects
Our team members are currently involved in several different research work in photovoltaic and solar energy materials.
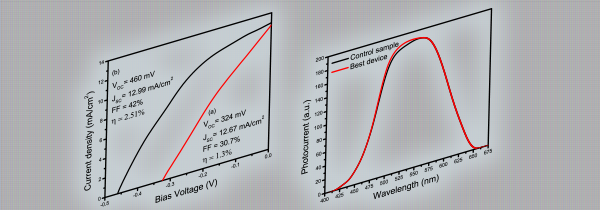
Development of highly efficient Cu₂O homojunction solar cells
We are studding the development of Cu2O homojunction solar cell by enhancing the optoelectrical properties of both n-Cu2O and p-Cu2O and interfacial properties of the Cu2O homojunction device. Electrodeposition technique is used to fabricate the device and n-Cu2O and p-Cu2O thin films are grown in acetate and lactate bath respectively. Currently, developed homojunction solar cell structure of Ti/n-Cu2O/p-Cu2O/Au produced Voc of 460 mV, Jsc of 12.99 mA/cm2, FF of 42% and η = 2.51%, under AM 1.5 artificial illumination. This is the record high Jsc value for Cu2O homojunction solar cells, but Voc and FF are still poor. Currently, we are working to improve the Voc and FF of the device.
RP Wijesundera, LKADDS Gunawardhana and W Siripala, Electrodeposited Cu2O homojunction solar cells: Fabrication of a cell of high short circuit photocurrent, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 157, pp. 881–886 (2016)
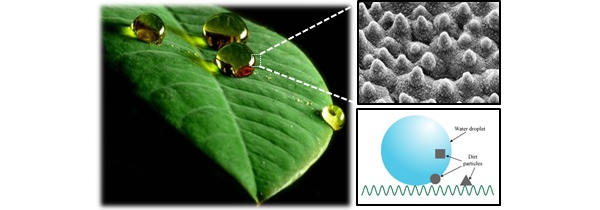
Wettability of electrodeposited semiconducting materials
Development of low-cost tin oxide thin films for solar cell applications using the method of electrodeposition
F. S. B. Kafi, B. H. Gunaratne, K. M. D. C. Jayathilaka and R. P. Wijesundera, Optimization of growth parameters of electrodeposited tin oxide thin films for PV applications, International Conference on Applied and Pure Sciences, 2023, Faculty of Science, University of Kelaniya, Sri Lanka, 191-197 (2023),
Development of TiO₂ based natural Dye Sensitized Solar Cells
DSSC research illuminate pathways to harnessing sunlight's potential, paving the way for brighter, cleaner, and more sustainable energy solutions. Our current investigation is centered on developing a DSSC utilizing TiO2 nanoparticles. In our investigation, we strive to elevate DSSC performance through an exploration of the electrical attributes of TiO2 layers, employing a range of natural dyes and methodologies. Effectiveness of DSSCs can be increased by modifying the cell, such as by adding metal nanoparticles. Copper stands out as a promising addition due to its localized surface plasmonic resonance (LSPR) effect, source abundance, low toxicity, and is inexpensive compared to noble metals. Dye Sensitized Solar Cells hold significant industrial importance as they offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution for harnessing solar energy on a large scale.
Low-dimensional metal oxide nanostructures
Growth of CZTS for CZTS/CdS solar cell applications
WTRS Fernando, KMDC Jayathilaka, RP Wijesundera and W Siripala, A Comparative Study: Sequentially and Single Step Electrodeposited CZTS Thin Films, Phys. Status Solidi A, 202200231 (2022)
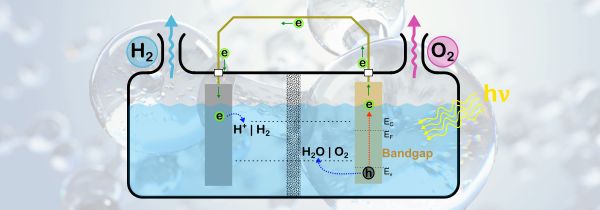
Hydrogen fuel from solar photocatalytic water splitting
Hydrogen is considered as the fuel of the 21st century and already the hydrogen economy has been set in progress. Hydrogen is the fuel having the highest energy density. The main objective of this research is to develop a device which can split water into hydrogen and oxygen efficiently using solar energy. This will allow producing hydrogen fuel that can be stored, transported and use when and where needed. For this purpose, in this research project, use of ultra low cost electrodeposited cuprous thin film electrodes will be envisaged.
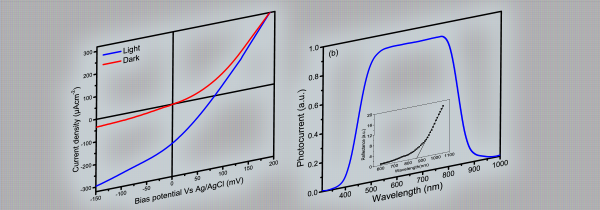
FSB Kafi, RP Wijesundera, W Siripala, Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting by Surface Modified Electrodeposited n‐Cu2O Thin Films, Phys. Status Solidi A, 2000330, (2020)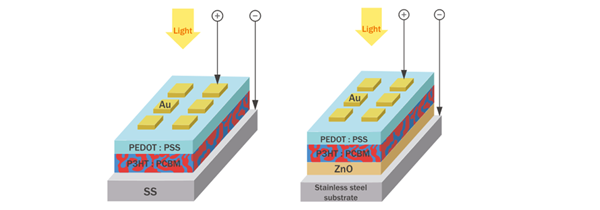
Development of P3HT/PCBM Organic Solar Cells
Polymer based organic solar cells (OSCs) are of tremendous interest as suitable candidates for producing clean and renewable energy in recent years. In this research, development of an efficient P3HT/PCBM organic solar cells is carrying out. Further zinc oxide (ZnO) and cuprous oxide (Cu2O) are studied as the electron selective transport layer (ESTL) and (PEDOT:PSS) is investigated as the hole transport layer (HTL) for enhancing the photoactive performance of the P3HT/PCBM organic solar cells.
DGK Kalara Namawardana, RM Geethanjana Wanigasekara, WTM Aruna PK Wanninayake, KMD Charith Jayathilaka, Ruwan P Wijesundera, Withana Siripala, Muhammad Imran Malik, Fabrication of inverted organic solar cells on stainless steel substrate with electrodeposited and spin coated ZnO buffer layers, Journal of Polymer Engineering, 42 (3), 233-242 (2022)
Synthes and characterization of CdS thin films
CdS thin films have emerged as a prominent subject of interest within the photovoltaic community due to their notable characteristics, such as wide optical band gap, efficient electron transport properties, and compatibility with economical fabrication methods. Our investigation is centered on exploring the potential of CdS thin films as a crucial element in the development of next-generation photovoltaic devices, specifically Copper Zinc Tin Sulfide (CZTS), with a primary focus on enhancing efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Our research initiatives encompass the following areas:
- Enhancement of CdS thin film deposition techniques to elevate film quality and ensure uniformity.
- Examination of innovative CZTS device architectures and material combinations aimed at enhancing photovoltaic efficiency and bolstering stability.
- Exploration of sustainable and environmentally friendly fabrication processes to address concerns associated with the use of CdS.
- As we progress in our investigations, we anticipate significant strides in CdS thin film technology, which will contribute to the realization of high-performance, economically viable, and environmentally sustainable photovoltaic devices.
We extend a warm invitation to collaborate with us as we collectively work towards shaping the trajectory of CdS thin films for a sustainable and prosperous future in photovoltaic applications.
